
Copper News: Strategies for Capitalising on the Copper Shortage Narrative
Jan 09, 2024
The world is experiencing a copper shortage, with limited production and increasing demand. This shortage will persist throughout 2023 and potentially for the rest of the decade. Copper is essential for various applications, including electrical equipment and industrial machinery, making it a crucial indicator of economic health. The scarcity of copper could signal worsening global inflationary pressures and lead central banks to maintain a hawkish stance.
Wood Mackenzie’s Vice President of Metals and Mining predicts significant deficits in copper production until 2030, attributing them to ongoing unrest in Peru and growing demand in the energy transition industry. The protests in Peru, which account for 10% of the global copper supply, have resulted in mining site closures. Chile, the largest copper producer globally, has also experienced a decline in production. While disruptions are common in the copper industry, some experts anticipate an increase in new mines in 2023.
Copper News: Electrification Boom and the Energy Transition Industry
The reopening of China, coupled with the growth in the automotive and energy transition sectors, has intensified the demand for copper, straining its resources. China’s economic recovery and pent-up market are expected to contribute to a copper deficit, which may last until a potential global economic recession in 2024-2025. As a result, copper prices could potentially double by then.
The broader trend of electrification, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) and charging infrastructure, will significantly drive copper demand. Copper is a critical component in electricity-related technologies, making it vital for the energy transition. The sales of EVs have been rapidly increasing, and the EV-charging ecosystem needs to expand accordingly. The energy transition industry’s growth in the automotive and transmission sectors poses a long-term supply issue for copper.
Copper News: Capitalizing on the Copper Shortage for Profit
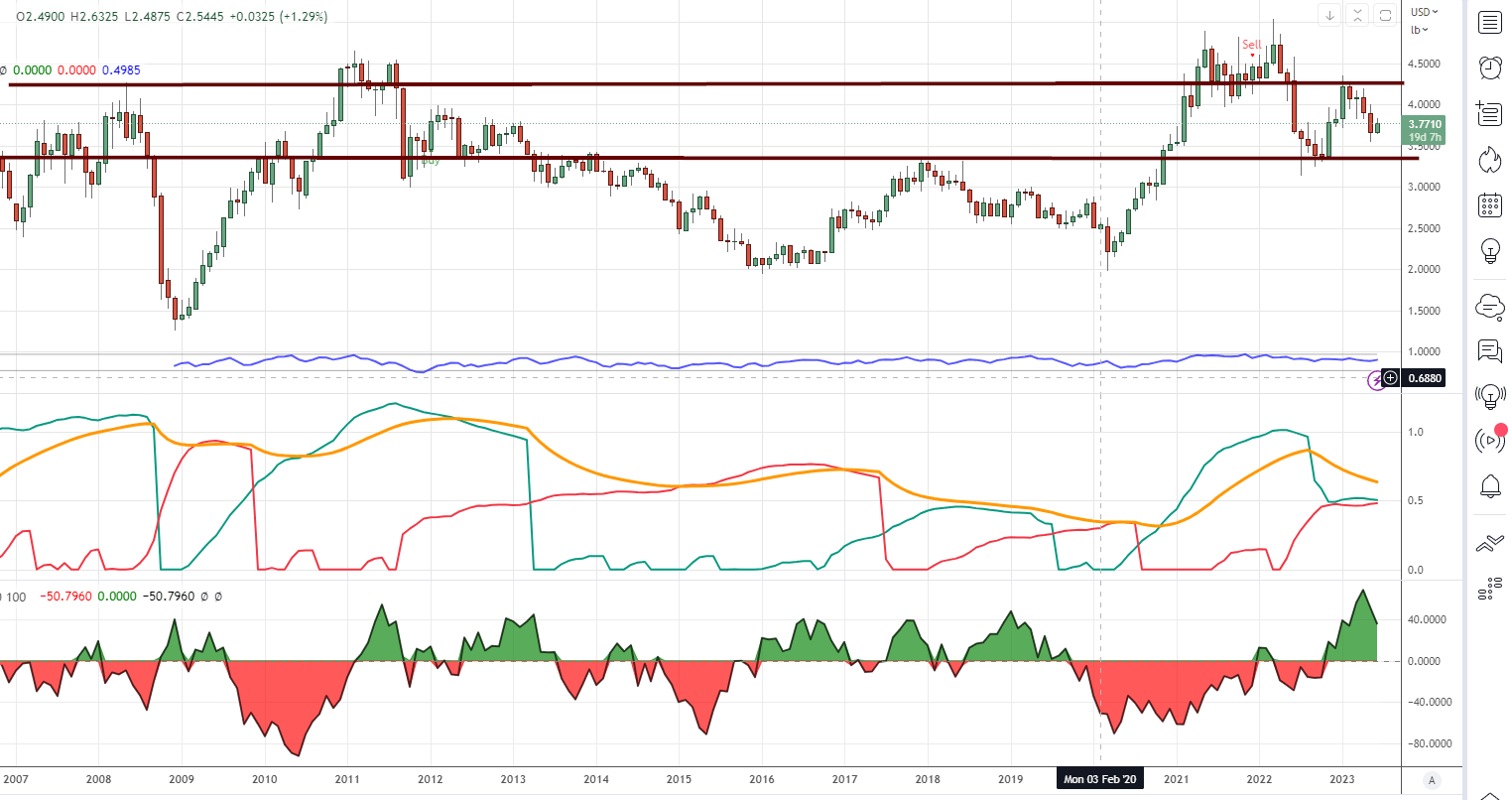
Copper is Consolidating, Gaining Momentum for an Upcoming Surge; Ensuring a Monthly Closure Above 3.70 is Crucial for Sustained Optimism. A Closure at or Exceeding 4.35 Expected to Propel It Towards New Heights. Moreover, it trades deep in the oversold territory on weekly charts, Aiming for an opportune breakout.
Enterprising Individuals May Partake in the Copper Market Through Investments in FCX, JJC, COPX, and Other Equities within this Sector.
Additional Insights: Projections and Global Implications
On the supply side, global markets are anticipated to experience a copper deficit throughout 2024, driven by increasingly strained South American supply streams and escalating demand pressures. Over the past six years, significant progress has been in applying machine learning to mineral-processing control, ensuring higher precision and consistency. By optimizing processing plant performance consistently, machine learning can enhance metal recoveries by an additional 2 to 4 per cent and increase throughput by 5 to 15 per cent.
Copper, a vital economic indicator due to its widespread use in electrical equipment and industrial machinery, is grappling with a worldwide shortage. This deficit is fueled by South American supply challenges and surging demand, potentially signalling worsening global inflationary pressures. The shortage might prompt central banks to maintain their hawkish stances for an extended period.
The world is experiencing a global copper shortage, with projections suggesting the shortfall could persist into the remainder of the decade. This aligns with copper’s role as a key economic indicator integrated into various technologies. A copper scarcity may indicate a worsening global inflationary environment, influencing central banks to extend their hawkish positions.
In summary, the copper market is currently dealing with a supply-demand imbalance, anticipating increased demand for its usage in diverse technologies and a corresponding decline in supply. Alongside psychological factors, this sets a bullish long-term outlook for copper.
Copper News: Factors challenging South American supply streams in 2024
Several factors are challenging South American supply streams in 2024.
Firstly, the global freight recession is expected to continue throughout 2024, with soft pricing in the shipping sector due to capacity in the logistics sector outstripping weaker demand. This is causing financial stress in the trucking sector and is expected to lead to lower freight orders and revenue.
Secondly, more than half of logistics managers do not expect the supply chain to return to normal until 2024 or after. This is due to ongoing global supply chain problems that have resulted in bloated inventories and packed warehouses, leading to a significant increase in warehouse prices.
Thirdly, the labour shortage in the supply chain industry is slowing the movement of goods and increasing costs. Supply chain leaders are exploring innovative solutions such as automation and workforce development programs to tackle this issue. However, rising costs, driven by inflation and rising energy prices, are a significant challenge for supply chains in 2024.
Lastly, South American power markets could face challenges if predictions of a moderate El Niño pattern materialize. This could increase power demand and prices, further strain the supply chain.
These factors, combined with the ongoing effects of the pandemic and extreme weather events, pose significant challenges to South American supply streams in 2024.
Conclusion
The global copper shortage, driven by limited production and increasing demand, will persist throughout 2023 and potentially beyond. This scarcity of copper has significant implications for economic health, inflationary pressures, and central bank policies. Wood Mackenzie’s forecast of copper deficits until 2030 highlights ongoing unrest in Peru and growing demand in the energy transition industry as contributing factors. The reopening of China, coupled with the electrification boom and the growth of the energy transition sector, further intensifies the demand for copper. This trend, driven by electric vehicles and charging infrastructure, poses a long-term supply issue. Considering the limited production and rising demand, investing in copper offers the potential for high returns.
The supply challenges in South America are multifaceted, encompassing a global freight recession, ongoing global supply chain problems, a labour shortage in the supply chain industry, and potential challenges in South American power markets due to predictions of a moderate El Niño pattern. These factors, combined with the ongoing effects of the pandemic and extreme weather events, pose significant challenges to South American supply streams in 2024.
On the demand side, copper, a vital economic indicator due to its widespread use in electrical equipment and industrial machinery, is grappling with a worldwide shortage. This deficit is fueled by surging demand, potentially signalling worsening global inflationary pressures. The shortage might prompt central banks to maintain their hawkish stances for an extended period.
Furthermore, the world is experiencing a global copper shortage, with projections suggesting the shortfall could persist into the remainder of the decade. This aligns with copper’s role as a critical economic indicator integrated into various technologies. A copper scarcity may indicate a worsening global inflationary environment, influencing central banks to extend their hawkish positions.
In light of these factors, the long-term outlook for copper is bullish. The anticipated increase in demand for copper due to its usage in diverse technologies, coupled with the expected decline in supply, sets the stage for potential high returns for those investing in copper.
Exceptional Insights: Articles That Push the Boundaries of Knowledge

Stock Market Anxiety: Overcome Fear and Focus on Opportunity

Contrarian Thinking: The Power of Challenging the Status Quo

What is Market Behavior? It’s Not the Question—It’s Time to Act

Brain Control: Domination via Pleasure

Power vs Force: Understanding Why Power Consistently Prevails

Benefits of Investing Early: Wealth and Serenity

Contrarian Outlook: A Pathway to Breakthrough or Breakdown

9-5 Rat Race: Work Until You Die or Break Free?

Collective Euphoria: How Madness Fuels Financial Disaster

Strategic Ignorance: When Math Collides with Market Madness

Uptrend Stocks: Embracing the Renaissance of Market Prosperity

Overtrading: A Foolproof Recipe for Becoming a Burro in the Markets

Mob Psychology: Breaking Free to Achieve True Financial Success

What is the Bandwagon Effect? Exploring Its Impact



